Bulk Suggestion
Bulk ID:
jeszhangg/05.25.24-12:47PM
Accepted at: May, 31, 2024
11:04 p.m.
Author:
jeszhangg
Co-authors:
Stapedius
Related Deck:
1675118865074
Accepted
Rationale for new note
from jess
Text
What are the main duct-dependent congenital heart diseases (CHD)?
{{c1::transposition of great arteries}} {{c1::hypoplastic left heart syndrome}} {{c1::coarctation of aorta}}
{{c1::tricuspid atresia}}
{{c1::transposition of great arteries}} {{c1::hypoplastic left heart syndrome}} {{c1::coarctation of aorta}}
{{c1::tricuspid atresia}}
Text
What are the <u>main</u> <b>duct-dependent congenital heart diseases (CHD)?</b> <br><br>{{c1::transposition of great arteries}} {{c1::hypoplastic left heart syndrome}} {{c1::coarctation of aorta}}<br>{{c1::tricuspid atresia}}
Extra
Duct dependent diseases refer to a group of heart conditions that require patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) to sustain life.
Severe aortic stenosis, pulmonary stenosis and ToF can also be included alongside the conditions mentioned above.
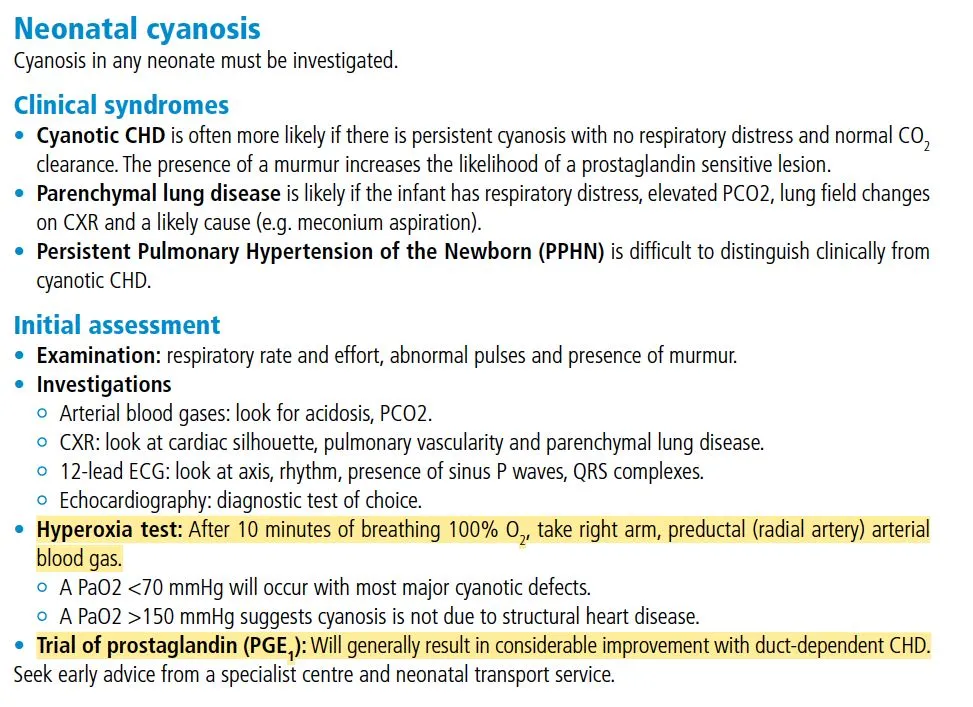
Severe aortic stenosis, pulmonary stenosis and ToF can also be included alongside the conditions mentioned above.
In TGA, right heart is pumping to aorta (systemic) without oxygenating, ∴ PDA can provide O2 via pulmonary artery
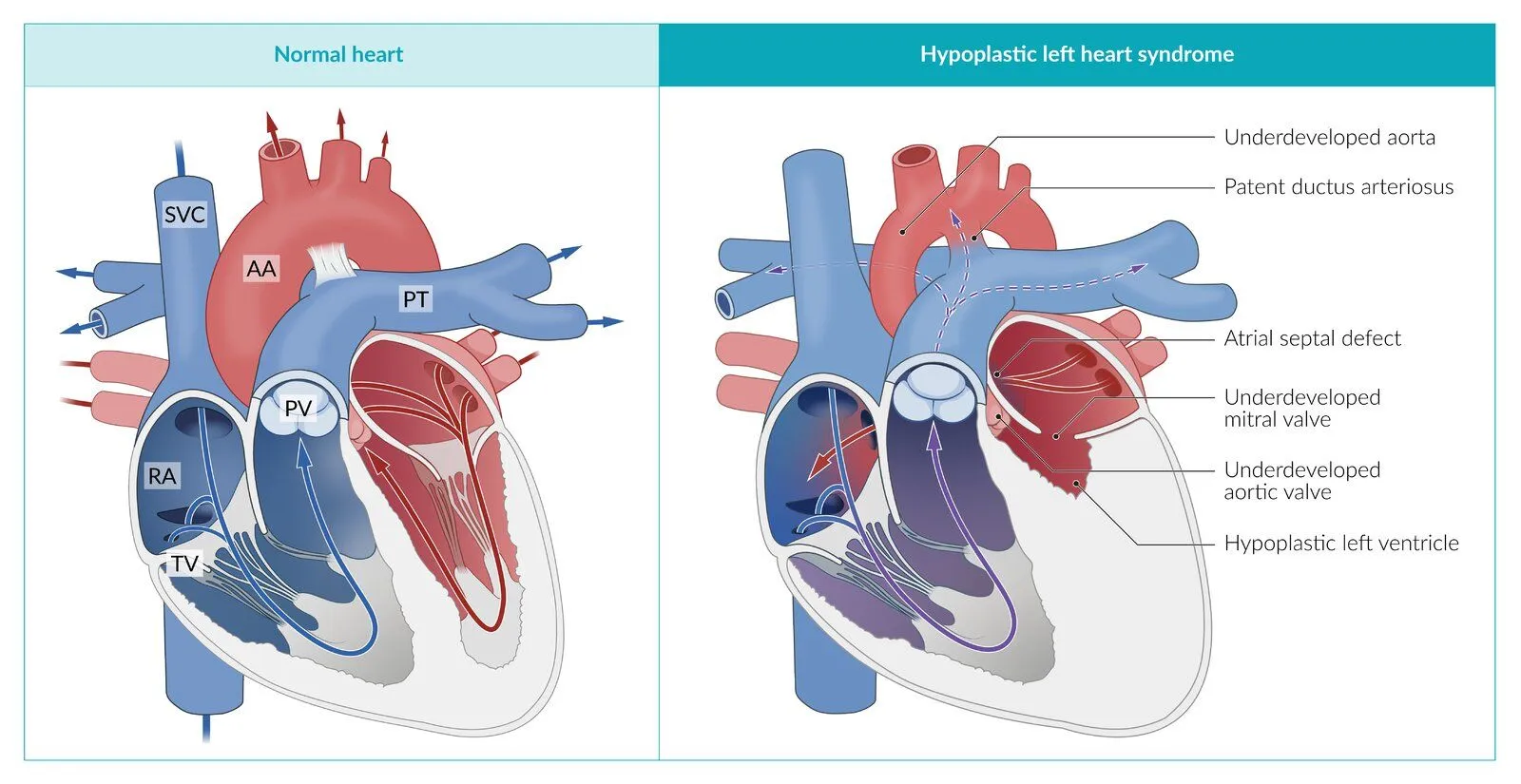
In hypoplastic left heart syndrome, left ventricle sucks, can't pump enough to aorta (systemic), so right heart pumps to pulmonary artery through PDA to aorta, supplying lungs and body
In coarctation of aorta, the narrowing in aorta severely reduces systemic CO ∴ PDA can bypass this, blood given to aorta from pulmonary artery
In tricuspid atresia, no blood is being pumped to lungs. ∴ PDA can allow blood from aorta → pulmonary artery to be oxygenated at lungs
In hypoplastic left heart syndrome, left ventricle sucks, can't pump enough to aorta (systemic), so right heart pumps to pulmonary artery through PDA to aorta, supplying lungs and body
In coarctation of aorta, the narrowing in aorta severely reduces systemic CO ∴ PDA can bypass this, blood given to aorta from pulmonary artery
In tricuspid atresia, no blood is being pumped to lungs. ∴ PDA can allow blood from aorta → pulmonary artery to be oxygenated at lungs


Extra
Duct dependent diseases refer to a group of heart conditions that require patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) to sustain life. <br><br>Severe aortic stenosis, pulmonary stenosis and ToF can also be included alongside the conditions mentioned above.<br><br><div class="centeredbox"><div class="leftalign">In TGA, right heart is pumping to aorta (systemic) without oxygenating, ∴ PDA can provide O<sub>2</sub> via pulmonary artery <br>In hypoplastic left heart syndrome, left ventricle sucks, can't pump enough to aorta (systemic), so right heart pumps to pulmonary artery through PDA to aorta, supplying lungs and body<br>In coarctation of aorta, the narrowing in aorta severely reduces systemic CO ∴ PDA can bypass this, blood given to aorta from pulmonary artery<br>In tricuspid atresia, no blood is being pumped to lungs. ∴ PDA can allow blood from aorta → pulmonary artery to be oxygenated at lungs<br></div></div><img src="7ace441e45674bbeb5de6c16803f787c.webp"><br><img src="fe6d72d6c10dc196bf82f50351380c35.webp"><br>
Extra (Synced)
Empty field
Extra (Synced)
Personal Notes
Empty field
Personal Notes
Missed Questions
Empty field
Missed Questions
eTG Complete
Empty field
eTG Complete
Talley & O'Connor
Empty field
Talley & O'Connor
Additional Resources
Empty field
Additional Resources
Additional Resources (Synced)
Empty field
Additional Resources (Synced)
Source
Cardiology. Paediatric Handbook RCH pg 170. Accessed May 21, 2024.
Cyanotic congenital heart defects. AMBOSS. https://next.amboss.com/us/article/Oo0IXS?m=a-bQDw. Accessed May 21, 2024
Cyanotic congenital heart defects. AMBOSS. https://next.amboss.com/us/article/Oo0IXS?m=a-bQDw. Accessed May 21, 2024
Source
Cardiology. Paediatric Handbook RCH pg 170. Accessed May 21, 2024.<br>Cyanotic congenital heart defects. AMBOSS. <a href="https://next.amboss.com/us/article/Oo0IXS?m=a-bQDw">https://next.amboss.com/us/article/Oo0IXS?m=a-bQDw</a>. Accessed May 21, 2024
One by one
Empty field
One by one
Tags
#Malleus_CM::#Resources_by_Rotation::Paediatrics
#Malleus_CM::#Subjects::Paediatrics::08_Cardiology::Congenital_Heart_Disease