Rejected at: Oct, 15, 2024
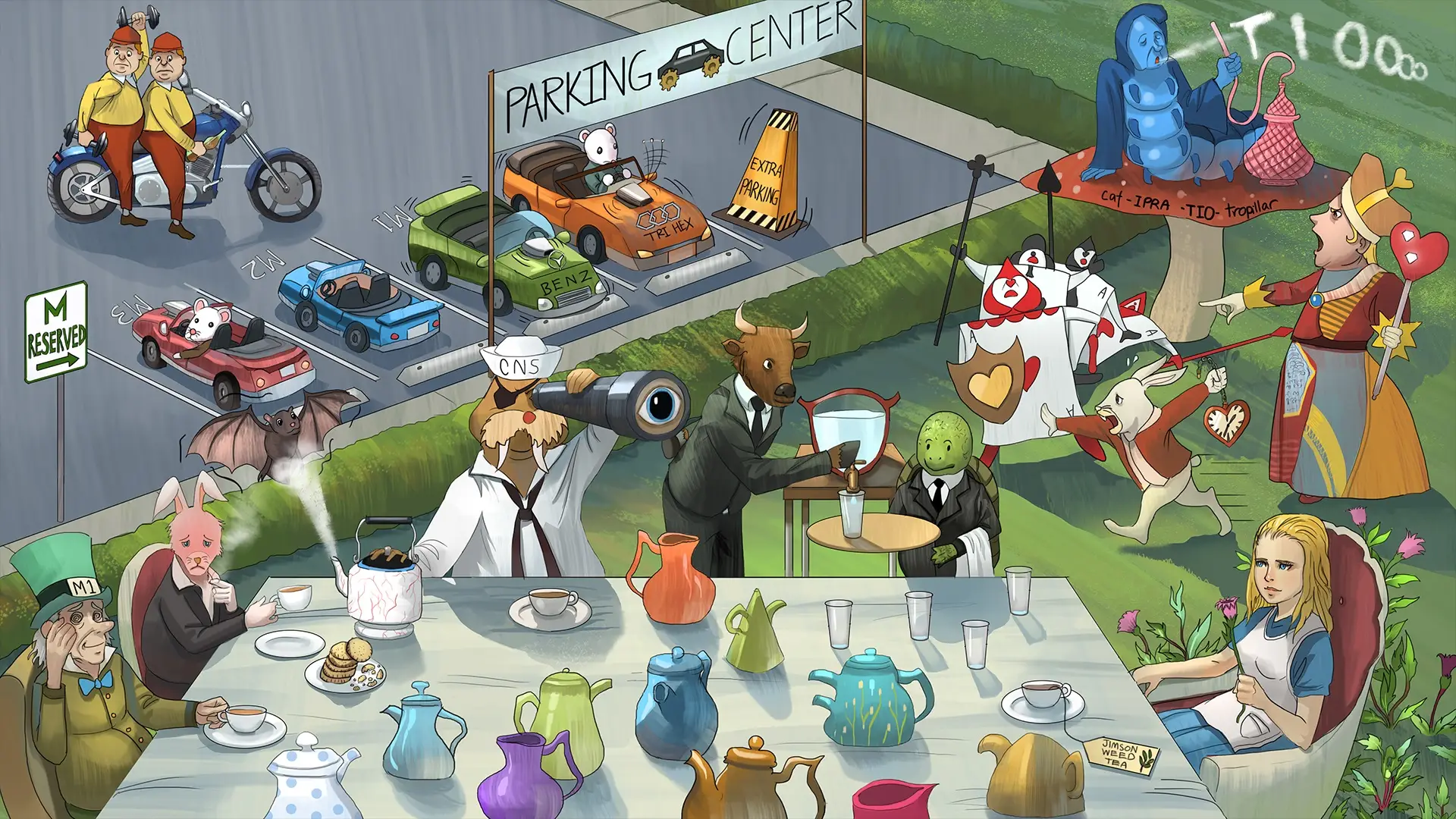
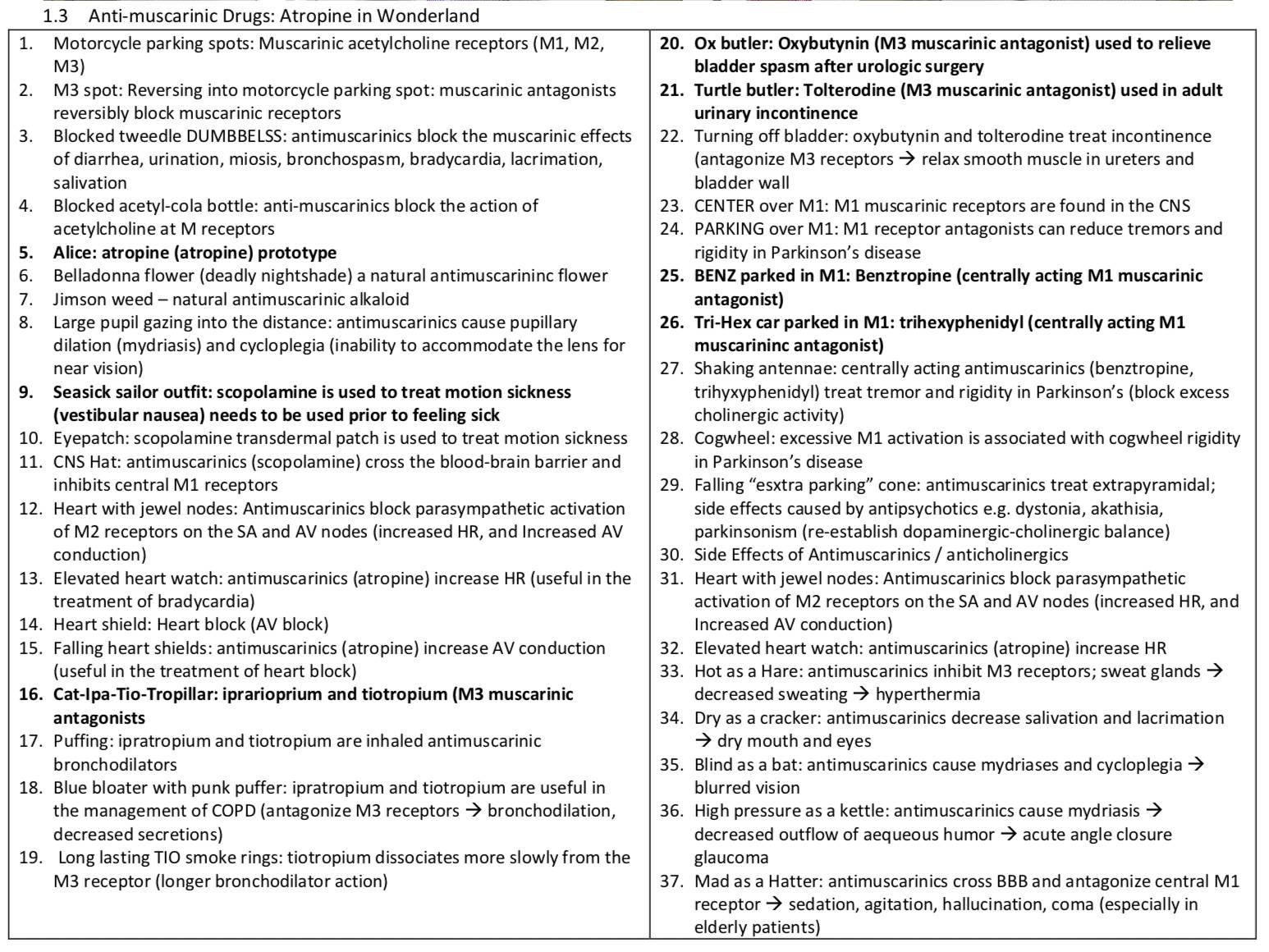
7:36 p.m.
Author:
ZKiun
Related Deck:
1649115753714
Rejected
Rationale for new note
Tests muscarinic vs cholinergic effects of myasthenia gravis and its therapy with ACHE inhibiotrs. Extra section explains rationale behind using *selecive* mucarinic antagonists.
Rejection reason
card submitted to wrong deck
Text
Selective {{c2::muscarinic}} antagonists can be used to reduce side effects of {{c1::cholinesterases}} in myasthenia gravis management.
Text
<b>Selective </b>{{c2::<b>muscarinic</b>}} <b>antagonists</b> can be used to reduce side effects of {{c1::cholinesterases}} in myasthenia gravis management.
Extra
e.g. glycopyrrolate, hyoscyamine, propantheline
ACHE inhibitors such as pyridostigmine inhibit the degradation of acetylcholine in the neuromuscular junction, prolonging the action of acetylcholine. Because it increases the concentration of acetylcholine, it increases the stimulation of both nicotinic receptors, which are impacted in MG, and muscarinic receptors, which are normal in MG. Therefore, acetylcholinesterase inhibitors improve skeletal muscle weakness but can cause muscarinic overstimulation of the smooth muscles and excessive glandular secretions (eg, diarrhea, diaphoresis, abdominal cramping, emesis).
Selective muscarinic antagonists (eg, glycopyrrolate, hyoscyamine, propantheline) can be used to reduce the adverse effects of cholinesterase inhibitors in sites where acetylcholine action is mediated by muscarinic receptors (ie, gastrointestinal tract). Because of their selectivity, these drugs improve adverse effects without affecting the action of cholinesterase inhibitors on skeletal muscle.
Extra
e.g. <i>glycopyrrolate, hyoscyamine, propantheline<br></i><br><div>ACHE inhibitors such as pyridostigmine inhibit the degradation of acetylcholine in the neuromuscular junction, prolonging the action of acetylcholine. Because it increases the concentration of acetylcholine, it increases the stimulation of both nicotinic receptors, which are impacted in MG, and muscarinic receptors, which are normal in MG. Therefore, acetylcholinesterase inhibitors improve skeletal muscle weakness but can cause muscarinic overstimulation of the smooth muscles and excessive glandular secretions (eg, diarrhea, diaphoresis, abdominal cramping, emesis).</div><div>Selective muscarinic antagonists (eg, glycopyrrolate, hyoscyamine, propantheline) can be used to reduce the adverse effects of cholinesterase inhibitors in sites where acetylcholine action is mediated by muscarinic receptors (ie, gastrointestinal tract). Because of their selectivity, these drugs improve adverse effects without affecting the action of cholinesterase inhibitors on skeletal muscle.</div>
Lecture Notes
Empty field
Lecture Notes
Missed Questions
Empty field
Missed Questions
Pathoma
Empty field
Pathoma
Boards and Beyond
Empty field
Boards and Beyond
First Aid
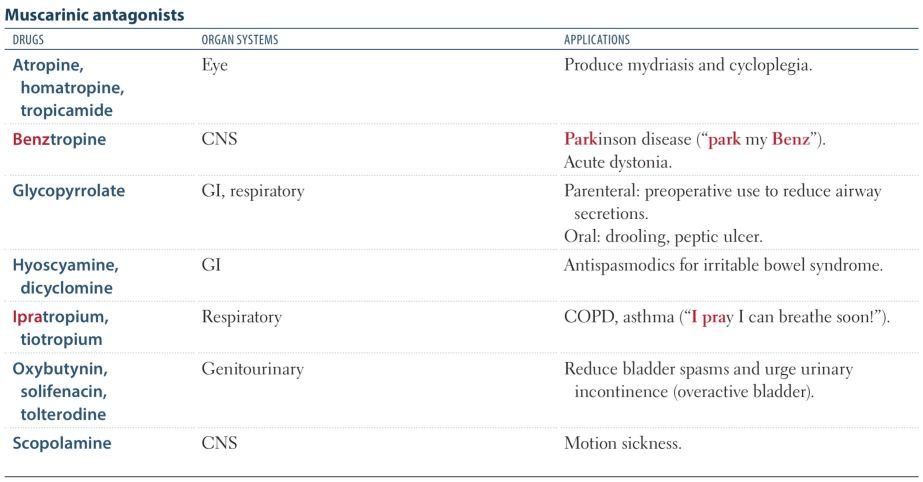
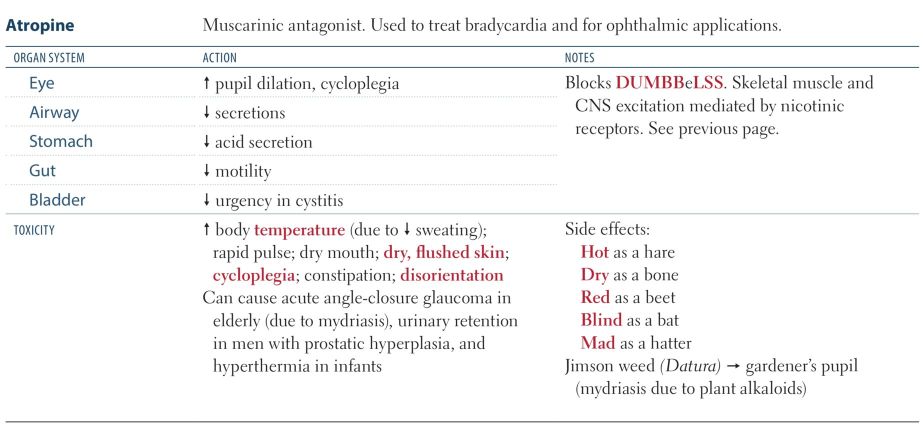


First Aid
<img src="paste-598503692697603.jpg"><img src="paste-600170140008451.jpg">
Sketchy
Sketchy
<img alt="Lesson Review" src="05cfae2f3d36cd93edb5537c2aac9eae.webp"><br><img src="Screen Shot 2019-09-23 at 9.15.51 AM.png"><br><a href="https://dashboard.sketchy.com/study/medical/courses/medical-pharmacology/units/medical-pharmacology-autonomic-drugs/videos/medical-pharmacology-autonomic-drugs-parasympathetic-muscarinic-antagonists?utm_source=anki&utm_medium=partnership&utm_campaign=february_update&utm_content=medical">Watch Muscarinic Antagonists</a>
Sketchy 2
Empty field
Sketchy 2
Sketchy Extra
Empty field
Sketchy Extra
Picmonic
Empty field
Picmonic
Pixorize
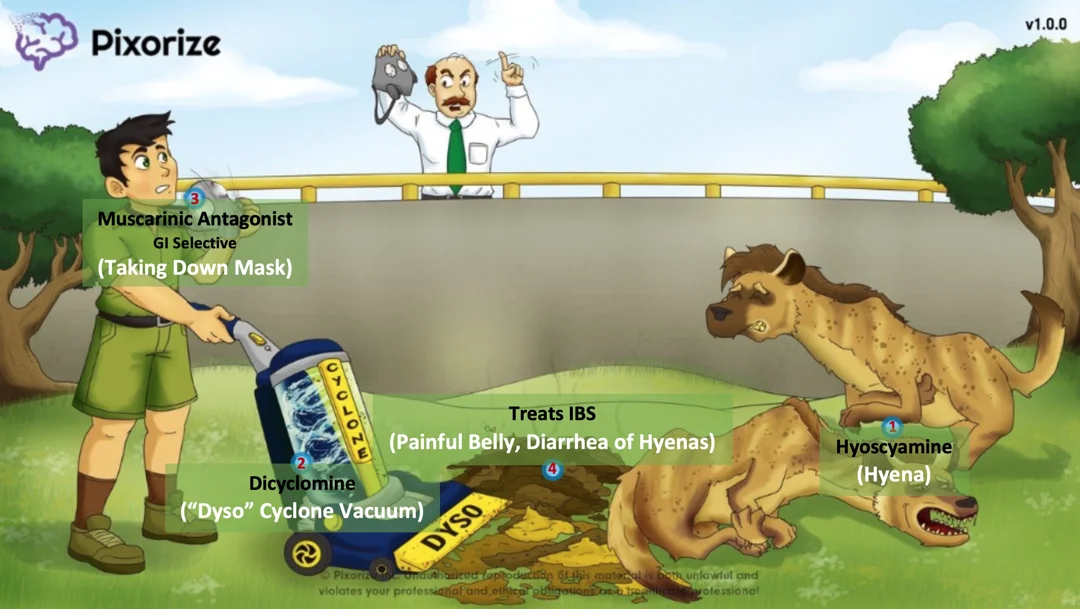








Pixorize
<img class="resizer" src="63c286d6506be8a6b99b2d4337b8efa3.webp"><br><img class="resizer" src="541cfd33da4d4835f4d7915d9dbf44ad.webp"><div><img src="fe65f091510b1cb6413117db0a436f30.webp" class="resizer"><br><img src="3a6e3aa234100c92952362c89493f902.webp" class="resizer"><br></div>
Physeo
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
Physeo
<img src="04012021_1146 (33).jpg"><img src="04012021_1146 (34).jpg"><img src="04012021_1146 (35).jpg"><br><img src="1002_05012021 (10).jpg">
Bootcamp
<a href="https://app.bootcamp.com/med-school/pharmacology/videos/autonomic-system?index=18">Watch associated Bootcamp video - Muscarinic Antagonists</a>
OME
OME
<div class="ome-widget"><a href="https://meded.cat/3zg8qKf"><img src="fa292137d0a7f96487bfeda4129a4017.webp"></a></div><br>
Additional Resources
Empty field
Additional Resources
One by one
Empty field
One by one
Tags
!AK_UpdateTags::Step1decks::Zanki-Pharmacology
#AK_Original_Decks::Step_1::Zanki_Pharmacology
#AK_Step1_v12::#B&B::15_Neuro::04_ANS::03_ANS_Drugs-_Acetylcholine
#AK_Step1_v12::#Bootcamp::Pharmacology::03_Autonomic_System::09_Muscarinic_Antagonists
#AK_Step1_v12::#FirstAid::05_Pharmacology::02_Autonomic_Drugs::08_Muscarinic_Antagonists::*Basics
#AK_Step1_v12::#OME_banner
#AK_Step1_v12::#Physeo::09_Pharm::16_Autonomic_Pharm::10_Indirect_Cholinergic_Agonists
#AK_Step1_v12::#Physeo::^physeo_image_update
#AK_Step1_v12::#Pixorize::03_Pharmacology::03_Anticholinergics::02_Glycopyrrolate
#AK_Step1_v12::#Pixorize::03_Pharmacology::03_Anticholinergics::03_Hyoscyamine_&_Dicyclomine
#AK_Step1_v12::#SketchyPharm::01_Autonomic_Drugs::01_Parasympathetic::03_Muscarinic_antagonists
#AK_Step1_v12::#UWorld::COMLEX::25171
#AK_Step1_v12::#UWorld::Step::2062
#AK_Step1_v12::^Other::^EXPN::BGadd
#AK_Step1_v12::^Other::^EXPN::BGnonessentials
#AK_Step1_v12::^Other::^EXPN::Uworld
#AK_Step1_v12::^Other::^HighYield::4-LowerYield
#AK_Step2_v12::#B&B::16_Surgery_&_Anesthesia::02_Anesthesia::03_Neuromuscular_Blockers
#MissedQ::Step1::Pharmacology::Autonomic_Drugs::Cholinomimetic_agents::Anticholinesterases